In 2015, the world was a vastly different place in terms of technology. Smartphones were smart but not yet brilliant. Artificial Intelligence was exciting but mostly theoretical for the average person. Space travel was largely the domain of government agencies. And yet, in a short span of just ten years, we’ve witnessed a cascade of innovations that would have sounded like science fiction to most people back then.
The 2020s have proven that the exponential pace of technological advancement is not only real—it’s accelerating. What once seemed like fantasies whispered in tech forums or speculative science documentaries are now concrete realities, changing the way we live, communicate, heal, work, and even perceive reality itself.
In this article, we’re going to explore seven groundbreaking technological innovations that seemed nearly impossible—or at least wildly optimistic—just a decade ago. Each one is a testimony to human curiosity, relentless innovation, and our innate desire to reshape the boundaries of possibility.
1. Artificial Intelligence That Feels Human
Back in 2015, artificial intelligence was mostly synonymous with narrow, task-specific algorithms. Yes, we had machine learning, voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, and recommendation systems running behind the scenes—but real conversations with AI were robotic at best and outright frustrating at worst.
Fast forward to the mid-2020s, and AI has crossed an invisible threshold. Thanks to neural networks that have grown both in complexity and training data, today’s AI systems can hold fluid, contextual, and almost human-like conversations. They can write poetry, compose music, assist in coding, tutor students in math, and even empathize—at least to the extent that they can mimic emotional intelligence through language.
Large Language Models (LLMs), multimodal systems, and generative AI have created a paradigm shift. ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and other advanced AIs have not just entered public life—they’ve become integral to education, business, healthcare, and creativity.
What seemed impossible a decade ago—having a natural conversation with a machine—has become routine. And the pace of improvement shows no signs of slowing.
2. Quantum Computers That Actually Work
Quantum computing was long the dream of physicists and theorists. In 2015, it was still firmly in the realm of fragile, error-prone, laboratory-only curiosities. Theoretical advantages had been proven on paper, but building a quantum computer that could outperform classical ones on useful tasks was still seen as a distant goal—perhaps decades away.
Yet here we are, with companies like IBM, Google, and startups like Rigetti having built quantum processors that are no longer just proof of concept but are performing real calculations. While we haven’t yet reached the mythical “quantum supremacy” on all fronts, we’ve made undeniable strides.
Quantum computers today can simulate molecules, optimize financial models, and solve certain classes of problems faster than their classical counterparts. Error correction—once considered a major hurdle—has seen revolutionary advances, bringing us closer to stability and scalability.
In 2015, most people barely knew what a qubit was. Now, industries from pharmaceuticals to logistics are preparing to restructure their future around quantum breakthroughs.
3. Space Tourism: From Billionaire Fantasy to Launch Pad Reality
Ten years ago, if you’d told someone they’d be able to book a ticket to space (for the right price), you might’ve been laughed out of the room. Space travel was still almost entirely the domain of national agencies like NASA, Roscosmos, and the ESA.
And yet, the 2020s brought with them a renaissance in space exploration, led not by governments but by private companies—SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic, among others. These pioneers did what was once unthinkable: they made space tourism real.
We’ve seen civilians—teachers, artists, YouTubers, and scientists—travel to suborbital space, experience weightlessness, and return safely. SpaceX’s all-civilian Inspiration4 mission was a game changer, proving that space could be accessible beyond just astronauts and billionaires.
The cost is still high, and the risks remain—but the barrier has been broken. Space, once the final frontier, is slowly becoming a destination. Commercial space stations, lunar tourism, and Mars-bound colonization plans are not just dreams—they’re being engineered as we speak.
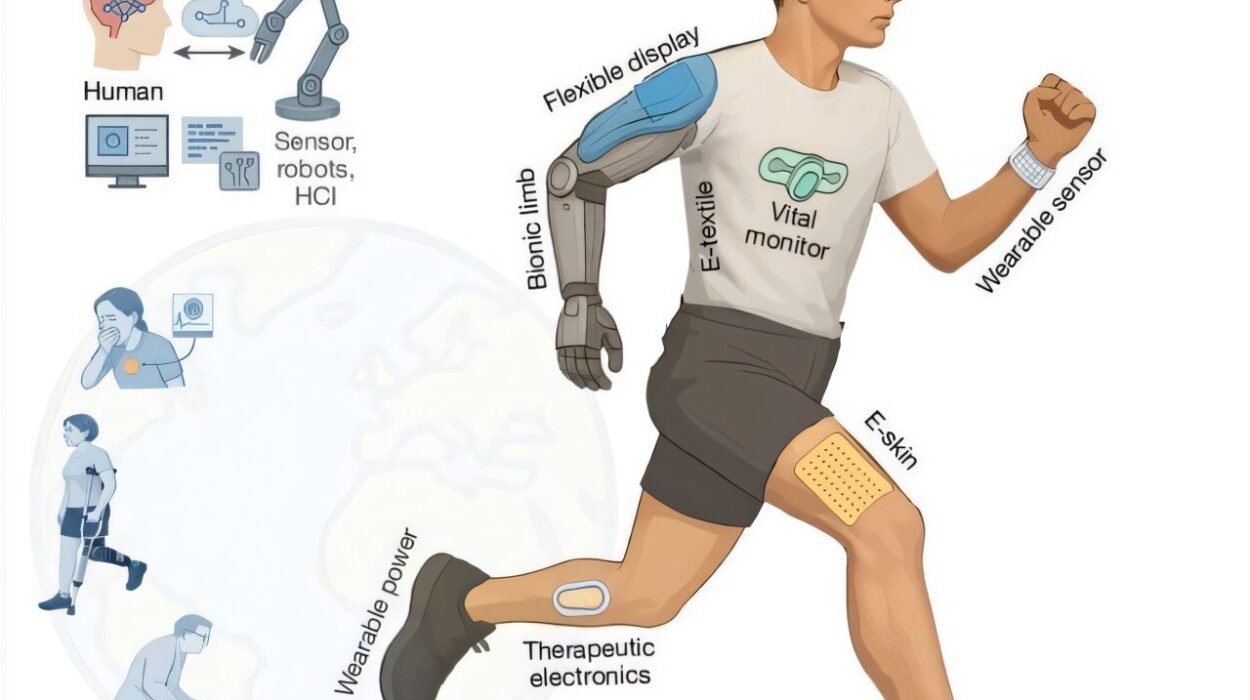
4. Brain-Computer Interfaces That Let You Type with Thought
In 2015, brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) were primarily explored in research labs, often requiring bulky EEG headsets or invasive brain surgery. The notion that someone could type words, move a cursor, or communicate simply by thinking about it seemed more like the plot of a cyberpunk novel than a technological reality.
Today, thanks to companies like Neuralink and academic breakthroughs across neuroscience, that vision is real.
BCIs have evolved into sophisticated devices that allow paralyzed individuals to communicate through mental signals alone. They can control robotic limbs, play video games, and even compose messages with astonishing precision and speed.
The ethical implications are vast—and so are the possibilities. In the future, we could see memory enhancement, thought-to-text composition, and direct mental search engines. Imagine Googling something with your brain, or speaking to your AI assistant silently, just by intention.
What once seemed impossible now sits at the edge of practical application. The human mind is no longer limited by biology—it’s entering the digital realm.
5. Digital Twins and the Dawn of the Mirror World
In 2015, the idea of creating full-scale digital replicas of physical systems—a concept called “digital twinning”—was in its infancy. While engineers used simulations and CAD models, the notion of a living, breathing digital twin of a person, city, or organ sounded like the stuff of sci-fi thrillers.
Today, digital twins are transforming how we build, diagnose, and manage everything from smart factories to human bodies. A digital twin of a heart can now be modeled in real-time to simulate how a patient will respond to surgery. Entire industrial plants operate with mirrored digital environments to optimize operations and predict maintenance.
We are entering the era of the “mirror world”—a persistent, interactive, spatial digital twin of Earth itself. This parallel reality, powered by IoT, AI, and 5G, allows simulations of everything: traffic flow, climate change, disease outbreaks, and supply chains.
For individuals, the future might include digital avatars that age with us, learn from our behaviors, and even make decisions on our behalf. These aren’t just copies—they’re intelligent, evolving extensions of our lives.
What once sounded like a philosophical or fictional idea—”What if we could live in a simulation?”—is now a tool being actively built, bit by bit, across every industry.
6. Regenerative Medicine and 3D-Printed Organs
In 2015, organ transplants were limited by donor availability, and the concept of “growing” an organ in a lab was mostly a biomedical fantasy. Tissue engineering was progressing, but practical application lagged behind.
Now, we are on the cusp of an organ revolution.
Thanks to advances in stem cell biology, bioprinting, and regenerative medicine, scientists have successfully printed functional human tissues—including skin, cartilage, and even miniature organs called organoids. These bio-structures are not only being used for research and drug testing but are paving the way for full organ fabrication.
Imagine printing a new liver tailored to your DNA. Or regrowing nerve tissues that restore movement after paralysis. In some trials, lab-grown bladders and windpipes have already been successfully implanted in patients.
The dream of defeating organ failure—not by replacing from donors but by regenerating from within—is now moving from theory into practice.
What was impossible a decade ago is now the foundation for a future where longevity, quality of life, and radical healing are redefined.
7. Fully Immersive Mixed Reality
In 2015, virtual reality (VR) was just beginning to shed its reputation as a gimmick. Devices like the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive were exciting, but limited in scope. Augmented reality (AR), meanwhile, was a novelty used in experimental apps or awkward smartphone overlays.
Today, we are stepping into the era of mixed reality—a seamless blending of the physical and digital worlds. With the release of devices like Apple Vision Pro and the refinement of Microsoft’s HoloLens, Magic Leap, and Meta’s XR platforms, people can now work, play, learn, and socialize in environments that feel both real and surreal.
These headsets allow users to interact with digital content as if it were physically present: a life-sized model of a human body for study, a floating spreadsheet for collaboration, or an entire simulated environment for mental wellness.
Mixed reality isn’t just about games—it’s changing medicine, design, architecture, and even relationships. People are holding virtual meetings in lifelike avatars, attending classes across continents, and simulating physical prototypes in real-time.
A decade ago, fully immersive environments seemed years—if not decades—away from being usable, let alone practical. Now, they are becoming an integral part of digital life.
The Ripple Effect: How These Innovations Are Intersecting
Each of these technologies is revolutionary on its own. But what’s truly transformative is how they intersect.
AI is powering quantum simulations. Digital twins are enhanced by real-time mixed reality visualization. Regenerative medicine benefits from AI-driven protein modeling and quantum chemistry. Brain-computer interfaces could one day operate in mixed-reality environments, providing seamless mind-to-machine integration.
This convergence is creating a kind of technological symbiosis where progress in one field catalyzes breakthroughs in others. We’re not just witnessing isolated innovations—we’re watching the birth of an entirely new human experience.
From Science Fiction to Daily Life
A striking theme across all these innovations is how deeply science fiction has influenced them. Neural interfaces, digital avatars, lifelike AI, immersive virtual worlds—these are the hallmarks of stories we once read in books or watched on screen.
What’s different now is that fiction is no longer just inspiring scientists—it’s being outpaced by them.
We live in a world where your phone contains more computing power than the rocket that put humans on the Moon. Where your AI assistant can write novels, answer legal questions, or design a video game. Where you could tour a digital twin of your heart while your brain interface sends real-time updates to your doctor.
It’s a thrilling, terrifying, and utterly remarkable time to be alive.
What the Next 10 Years May Bring
If the past decade has taught us anything, it’s that “impossible” is often just a matter of time.
In the next ten years, we could see commercial quantum advantage, mainstream mind-controlled devices, Mars settlements, fully bioprinted organs, and AI co-workers as standard parts of the human experience. We might unlock new dimensions of perception with brain-connected mixed-reality. We might simulate entire cities before building them.
We might even, as strange as it sounds, start to consider post-humanity—a world where biology, machine, and consciousness evolve together.
Conclusion: The New Possible
A decade ago, much of what we see today would’ve seemed implausible at best and delusional at worst. But the pace of innovation, once slow and linear, is now exponential. As each field feeds into the next, the edge of possibility keeps moving forward.
The greatest lesson? Never underestimate what human creativity can do when curiosity, collaboration, and courage collide. The future may be unpredictable—but one thing is certain:
What seems impossible today may just be tomorrow’s new normal.