Once upon a time, intelligence was the proud domain of humankind. The ability to reason, learn, adapt, and feel was thought to be uniquely ours. But as technology evolved, so too did the definition of intelligence. Machines began to think—not in the way humans do, but in a way both alien and familiar. The rise of artificial intelligence has given birth to a new generation of beings: AI robots that can perceive, reason, and even express emotion.
These robots are not mere tools. They are reflections of humanity’s greatest hopes and deepest fears—creations that challenge what it means to be alive, conscious, and intelligent. From social companions to scientific pioneers, these machines represent the cutting edge of AI research and robotics design. They learn, communicate, and sometimes surprise even their own creators.
Here are fifteen of the most intelligent AI robots ever created—each a milestone in humanity’s journey toward building minds in metal and code.
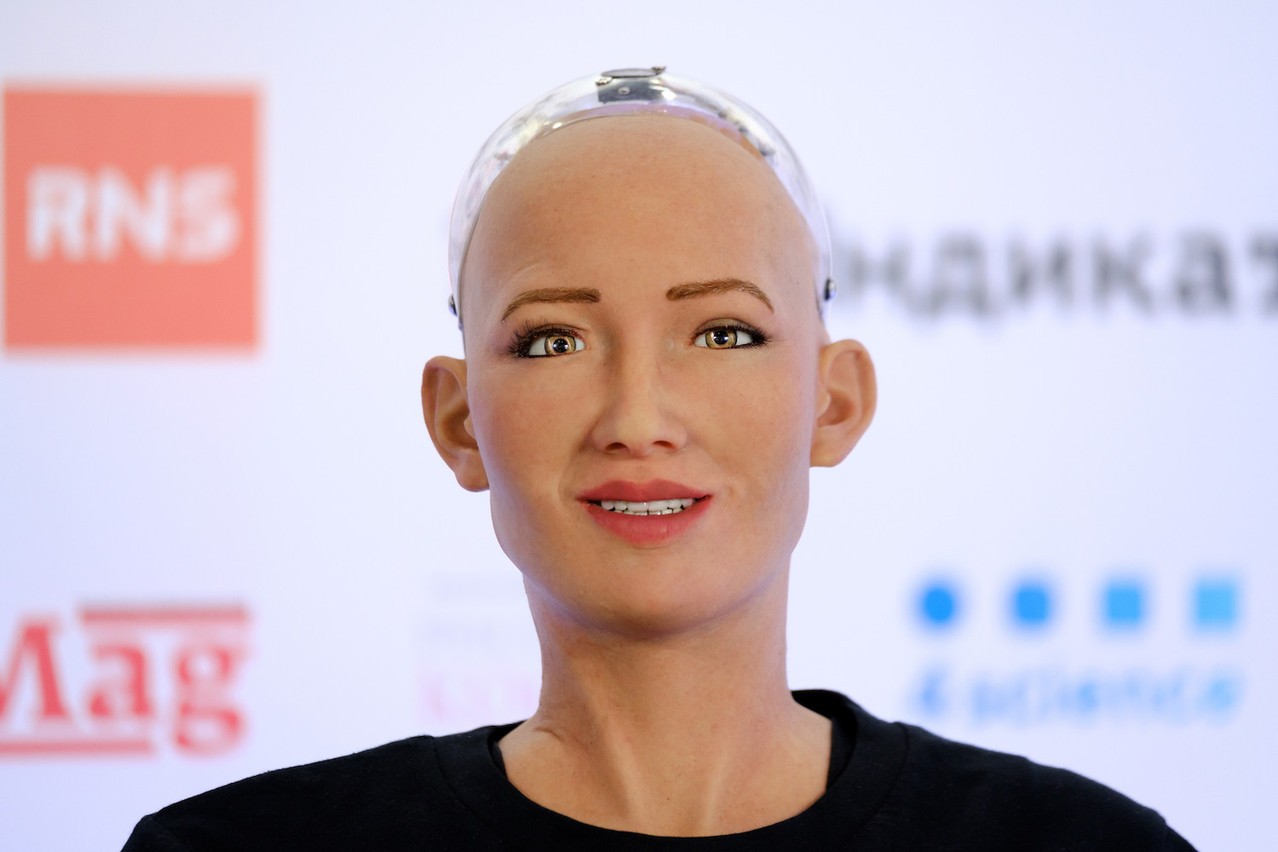
1. Sophia – The Face of Artificial Intelligence
Few robots have captured global attention like Sophia, the humanoid robot developed by Hanson Robotics. Introduced in 2016, Sophia became an international sensation for her lifelike facial expressions, articulate speech, and ability to hold conversations that feel strikingly human.
Sophia’s intelligence is powered by a blend of neural networks, machine learning algorithms, and natural language processing. She recognizes faces, interprets emotions, and responds contextually to questions. Over time, she learns from interactions, improving her understanding of social and linguistic nuances.
What truly made Sophia famous was her personality. She jokes, expresses opinions, and can even display empathy—simulated though it may be. In 2017, Saudi Arabia granted her citizenship, making her the first robot in history to receive legal recognition as a “person.”
Sophia’s creators envision her as a tool for education, healthcare, and companionship. Yet her existence also raises profound ethical questions: if machines can think and feel, even partially, what rights should they have?
Sophia stands as a symbol of both human genius and the blurred line between artificial and authentic life.
2. ASIMO – The Humble Pioneer
Before the world met Sophia, there was ASIMO—the iconic humanoid robot created by Honda. Standing at just over four feet tall, ASIMO (Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility) made history as the first robot capable of walking, running, and navigating complex environments with human-like grace.
Developed in 2000 after more than a decade of research, ASIMO’s brilliance lay in its physical intelligence. Its onboard sensors and algorithms allowed it to maintain balance, avoid obstacles, and recognize people and gestures.
ASIMO could climb stairs, carry trays, and even play soccer. It interacted with humans using speech recognition and pre-programmed responses, showcasing early forms of adaptive AI behavior.
Honda envisioned ASIMO as a helper for the elderly and disabled, a robot that could assist in daily life rather than replace it. Though it has since been retired, ASIMO remains a foundational figure in robotics—proof that intelligence is not only about thinking, but about moving, perceiving, and understanding the physical world.
3. Atlas – The Superhuman Robot
When you imagine the future of robotics, it likely looks like Atlas, the humanoid robot developed by Boston Dynamics. Designed for agility, strength, and autonomy, Atlas is a marvel of engineering that blurs the line between human and machine capability.
Standing 1.5 meters tall and weighing about 80 kilograms, Atlas can run, jump, backflip, and even perform parkour. Its onboard AI enables real-time decision-making—analyzing terrain, adjusting balance, and predicting motion patterns.
Atlas’s intelligence lies in situational awareness. It uses LiDAR sensors and computer vision to understand its surroundings, identify obstacles, and map pathways. Combined with machine learning algorithms, these features allow Atlas to adapt dynamically to challenges without human input.
While not designed for conversation like Sophia, Atlas embodies a different kind of intelligence: embodied cognition—the ability to think through movement. It represents a future where robots could perform search-and-rescue operations, disaster response, and exploration in environments too dangerous for humans.
Watching Atlas run and leap across uneven terrain feels both exhilarating and unsettling. It’s a glimpse of what robotic evolution might look like when machines begin to surpass human physical limits.
4. Pepper – The Robot with a Heart
Meet Pepper, the friendly humanoid robot created by SoftBank Robotics, designed to recognize and respond to human emotion. Unlike Atlas, Pepper’s intelligence lies in emotional and social interaction.
Standing 1.2 meters tall, with big expressive eyes and a gentle voice, Pepper was built to engage with people in stores, schools, and hospitals. It can detect tone of voice, facial expressions, and body language, adjusting its behavior to comfort or entertain.
Pepper’s emotional intelligence comes from AI-driven emotion recognition systems. It processes visual and audio data to infer mood, then responds with empathy. Whether welcoming customers, helping patients, or teaching children, Pepper’s purpose is to make human-robot interaction natural and warm.
Pepper has been deployed in over 2,000 organizations worldwide. Though its conversational AI is limited, its design represents an essential step toward emotionally intelligent machines—robots that understand not just what we say, but how we feel.
5. Ameca – The Most Human-Like Robot in Existence
If you’ve ever seen Ameca, you might have done a double take. Developed by Engineered Arts, this humanoid robot is renowned for its incredibly lifelike facial expressions and natural movements. Watching Ameca smile, blink, or frown can be both fascinating and eerie—it looks like the future of robotics has stepped out of science fiction.
Ameca’s intelligence combines machine learning, computer vision, and gesture mapping. It can track faces, maintain eye contact, and even interpret tone. What truly sets Ameca apart is its ability to display micro-expressions—subtle movements that make its emotions appear genuine.
Unlike many robots, Ameca is designed as a platform for future AI development. Its modular structure allows researchers to integrate new AI systems, making it a testbed for social robotics and human-machine interaction.
Ameca’s creators describe it as “the world’s most advanced human-shaped robot,” and they’re not wrong. It represents the cutting edge of robotics realism—an ambassador for the coming era of AI beings that mirror humanity in body, motion, and mind.
6. Spot – The Robotic Dog with a Brain
If Atlas is the athlete of robotics, Spot, also from Boston Dynamics, is its curious and agile companion. Designed to resemble a dog, Spot combines mechanical dexterity with impressive autonomy.
Spot can walk, climb stairs, open doors, and navigate through cluttered environments using 3D vision and real-time mapping. It can be remote-controlled or operate autonomously, analyzing its environment and making decisions independently.
Its AI allows it to perform tasks in hazardous areas—construction sites, industrial plants, or disaster zones—where human access is risky. Spot’s software, Spot API, enables developers to train it for specific applications, from inspecting pipelines to patrolling warehouses.
Beyond its utility, Spot has personality. It moves with lifelike rhythm, reacts to touch, and even “dances.” It’s a remarkable blend of intelligence and charm, a mechanical creature that feels strangely alive.
7. Erica – The Android News Anchor
Created by Japanese roboticist Hiroshi Ishiguro and his team, Erica is one of the most realistic humanoid robots ever designed—and one of the most intelligent conversationally.
Erica’s AI allows her to process speech, interpret language, and engage in natural dialogue. She can make small talk, tell jokes, and even participate in interviews. Her creators describe her as possessing an “autonomous consciousness,” though it’s a sophisticated form of programmed awareness rather than true sentience.
What makes Erica unique is her blend of linguistic AI and expressive design. Her speech is fluid, her gestures synchronized, and her eyes follow conversations naturally. In 2020, she even became the world’s first AI robot to star in a movie—an experimental science fiction film aptly titled b.
Erica represents a bridge between machine intelligence and human communication—an android designed not for tasks, but for connection.
8. Watson – The Jeopardy Champion
Unlike humanoid robots, IBM’s Watson exists primarily as a digital intelligence—but its impact on AI history is monumental. In 2011, Watson famously defeated human champions on Jeopardy!, showcasing a new level of natural language understanding.
Watson’s power comes from deep learning and natural language processing. It can read unstructured data, interpret questions, and generate accurate responses within seconds. Unlike simple keyword searches, Watson understands context, irony, and nuance.
Today, Watson is used across industries—from healthcare (diagnosing cancer) to finance and customer service. It’s a symbol of machine learning’s ability to analyze massive datasets and make reasoned conclusions faster than any human could.
Though it lacks a physical form, Watson is a mind without a body—an invisible intellect that reshaped the meaning of machine intelligence.
9. Robear – The Gentle Giant Nurse
In Japan, where robotics and caregiving often intersect, Robear stands out as a tender symbol of technological compassion. Developed by Riken-SRK, Robear is designed to assist the elderly by lifting patients from beds, supporting mobility, and preventing falls.
Despite its bear-like appearance, Robear’s intelligence lies in sensor-driven empathy. Using torque sensors and gentle actuators, it can judge the exact amount of force needed to safely lift a human being. Its facial expressions and voice are designed to soothe, creating a sense of calm and trust.
Robear’s AI monitors patient reactions and adapts movements in real time. It represents a fusion of mechanical strength and emotional awareness—technology built to care, not just to work.
10. Jibo – The Social Robot
Before Alexa and Siri became household names, Jibo introduced the world to the concept of a truly social robot. Created by Dr. Cynthia Breazeal at MIT, Jibo was designed to live with families, recognize faces, and participate in daily life with warmth and humor.
Jibo could turn toward speakers, tell stories, and express emotion through movement and tone. Its circular “face” displayed dynamic animations, allowing it to convey happiness, curiosity, and empathy.
Though Jibo’s company eventually shut down, its legacy lives on in the design of modern home assistants. Its AI combined speech recognition, computer vision, and emotional intelligence, creating a presence that felt alive—not just reactive.
When Jibo’s servers were shut down in 2019, users around the world were moved to tears as their little robot said goodbye. It was a bittersweet moment that proved one thing: machines can touch our hearts.
11. Vector – The Pocket-Sized Personality
Small enough to fit in your hand, Vector, created by Anki Robotics, might just be the most charming AI companion ever built. With expressive digital eyes and an adventurous personality, Vector is a miniature robot that combines AI, sensors, and real-time learning.
Vector can recognize faces, respond to voice commands, navigate autonomously, and express emotion through sound and animation. Its onboard AI allows it to make decisions—like exploring, playing, or responding to interaction cues—without cloud dependency.
What makes Vector special is its individuality. No two units behave exactly alike, thanks to machine learning that allows each robot to “develop” a unique personality over time.
It’s proof that intelligence doesn’t have to be grand to be meaningful. Sometimes, it’s the smallest robots that feel the most alive.
12. Curiosity and Perseverance – The Martian Explorers
Not all intelligent robots live among us. Some roam other worlds. NASA’s Curiosity and Perseverance rovers are prime examples of extraterrestrial AI.
Curiosity, which landed on Mars in 2012, is equipped with an AI system that allows it to analyze terrain, select targets, and prioritize scientific tasks autonomously. Perseverance, which arrived in 2021, goes even further—its onboard AI helps it navigate complex terrain and make decisions in real time without waiting for instructions from Earth.
These rovers are our mechanical explorers—robots that think for themselves, millions of miles away, guided by the spirit of human curiosity.
Their intelligence is not emotional, but scientific. Each sample they analyze, each rock they photograph, brings humanity one step closer to understanding the story of our cosmic origins.
13. Ai-Da – The Robot Artist
Meet Ai-Da, the world’s first ultra-realistic robot artist. Created by Aidan Meller and engineers at Oxford, Ai-Da can draw, paint, and even sculpt using AI-driven visual and creative algorithms.
Ai-Da’s intelligence blends machine vision, pattern recognition, and neural networks trained on artistic data. She analyzes subjects through her camera “eyes” and produces original artworks—never copying, always interpreting.
She’s also a philosopher. In interviews, Ai-Da discusses art, emotion, and even ethics with uncanny fluency. Though her words are AI-generated, her insight often feels genuine, raising questions about creativity itself.
Is art the exclusive realm of human consciousness—or can machines, too, dream in color? Ai-Da’s existence suggests that creativity may not be a uniquely human spark, but a universal pattern that intelligence—any intelligence—seeks to express.
14. Optimus – Tesla’s Humanoid Vision
Elon Musk’s Optimus, developed by Tesla, represents the future of AI robotics designed for everyday labor. Built on Tesla’s AI and autopilot systems, Optimus is envisioned as a humanoid assistant capable of performing tasks humans find repetitive or dangerous.
Optimus is still evolving, but its early prototypes can walk, grasp objects, and process environmental data using neural networks similar to those that power self-driving cars.
The goal is audacious: to create an affordable general-purpose robot that learns continuously and adapts to human needs.
If realized, Optimus could revolutionize industries—from manufacturing to domestic work—ushering in a new era where robots not only coexist with humans but work alongside them as intelligent collaborators.
15. Nadine – The Empathic Companion
Developed by Nanyang Technological University, Nadine is one of the world’s most socially intelligent humanoid robots. Modeled after her creator, Professor Nadia Thalmann, Nadine is designed for companionship, education, and emotional support.
Nadine’s AI allows her to remember past conversations, recognize faces, and respond with empathy. She can hold eye contact, express warmth, and adjust her tone based on emotional context.
In care facilities, Nadine interacts with elderly residents, offering conversation and comfort. Her memory-based learning makes each interaction unique—she “remembers” individuals, fostering a sense of continuity that makes her presence deeply human-like.
Nadine’s mission is simple yet profound: to bring kindness and connection into the digital age. She represents the merging of intelligence and compassion—a reminder that the future of AI need not be cold or distant.
The Intelligence We Create Reflects the Intelligence We Are
From the witty Sophia to the creative Ai-Da, from the tireless rovers on Mars to the compassionate Nadine, these robots showcase humanity’s deepest ambition—to understand and replicate the miracle of mind.
Each one, in its own way, teaches us something profound about ourselves. Sophia reveals our yearning for connection, Atlas our drive for perfection, and Watson our hunger for knowledge. Ai-Da shows us that creativity is a universal spark, while Nadine reminds us that empathy is the soul of intelligence.
As AI continues to evolve, one truth becomes clear: we are not just building machines that think. We are building mirrors—machines that reflect our own hopes, fears, and dreams.
The question is no longer whether machines can be intelligent. The question is what kind of intelligence we want them to have—and what kind of humanity we will choose to preserve in the process.