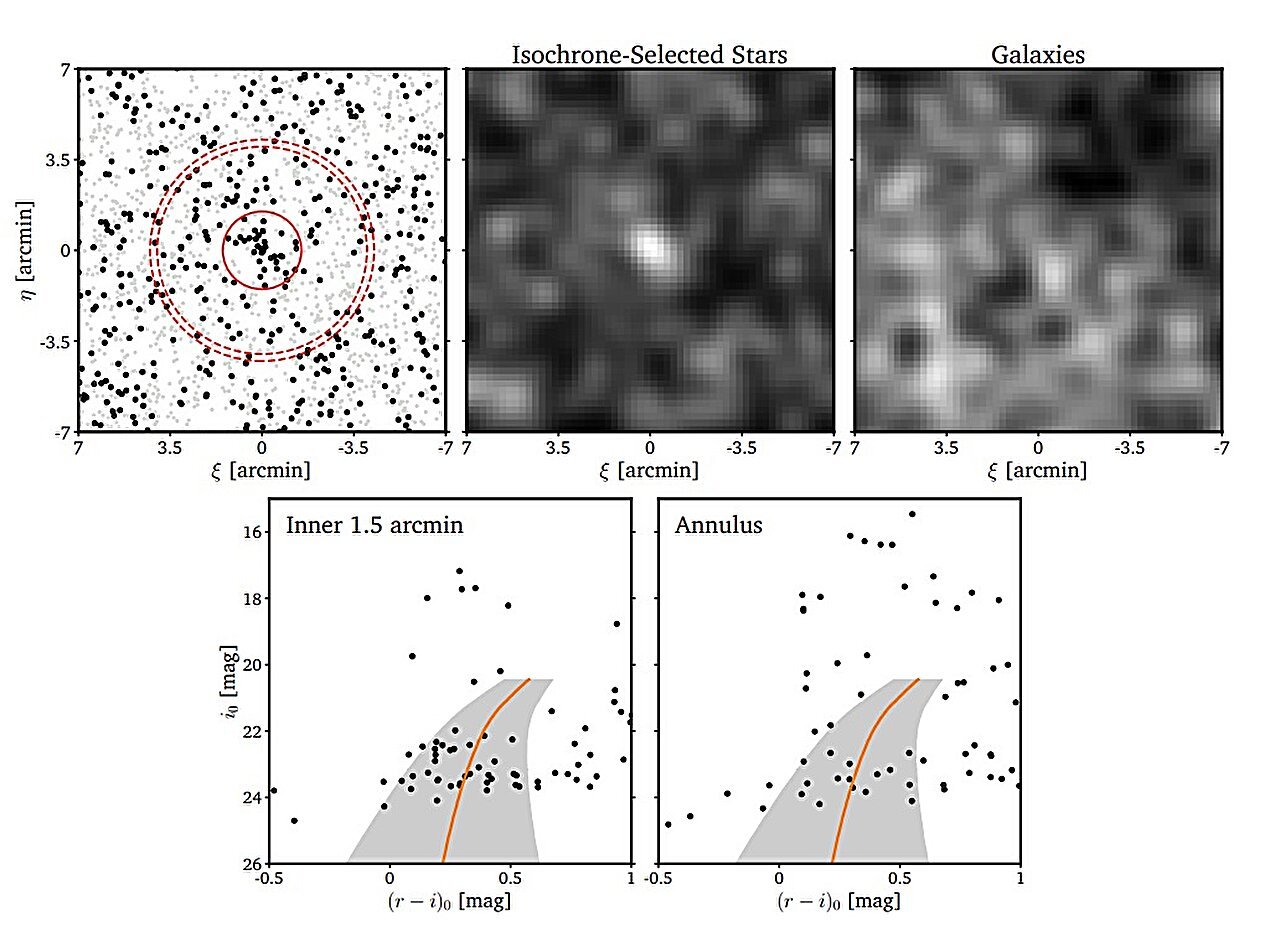
An international team of astronomers has made an exciting discovery with the identification of a new dwarf galaxy, which they have named Pegasus VII. Situated about 2.4 million light years from Earth, Pegasus VII was uncovered through the Ultraviolet Near-Infrared Optical Northern Survey (UNIONS). This breakthrough, detailed in a research paper published on February 13 on the arXiv preprint server, offers new insights into the nature of dwarf galaxies and their relationship with larger galaxies.
Dwarf galaxies are small, low-luminosity stellar systems that typically contain only a few billion stars. Despite their diminutive size and mass, these galaxies hold significant interest for astronomers because they are believed to provide crucial information about the processes involved in galaxy formation and evolution. The interactions between dwarf galaxies and larger galaxies often play a key role in shaping the former, influencing their star formation rates and overall structure. As a result, dwarf galaxies are considered natural laboratories for studying these complex interactions.
Discovery in the Halo of Andromeda
Dwarf galaxies are frequently found in the halo of larger galaxies, where they may be in the process of being absorbed or influenced by the gravitational pull of their more massive neighbors. One of the best places to look for these galaxies is the halo of the Andromeda Galaxy, also known as Messier 31 (M31). Due to its relative proximity to our Milky Way, Andromeda provides a unique opportunity for astronomers to study these objects in detail.
The UNIONS survey is the most comprehensive and deepest survey currently available for exploring the farthest reaches of Andromeda’s halo, and it has proven invaluable in detecting previously unseen dwarf galaxies. The team of astronomers, led by Simon E. T. Smith from the University of Victoria in Canada, focused their efforts on the survey’s ri photometric catalogs to identify faint and distant objects. Their search paid off with the discovery of Pegasus VII, a new dwarf galaxy member of the M31 sub-group.
The team confirmed the discovery with follow-up imaging taken from both the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope and the Gemini-North Telescope. This additional data provided crucial support in verifying the galaxy’s existence and properties.
Position and Physical Characteristics
Pegasus VII is situated approximately 1.08 million light years away from Andromeda, placing it just on the cusp of crossing the virial radius of M31. The virial radius marks the boundary within which the gravitational influence of Andromeda is dominant. Being so close to this threshold means that Pegasus VII could be on the verge of an interaction with Andromeda, which may significantly alter its structure or future evolution.
In terms of its physical characteristics, Pegasus VII is quite faint, with an absolute V-band magnitude of −5.7, making it the faintest known dwarf galaxy satellite of Andromeda. The galaxy’s central surface brightness is recorded at 27.3 mag/arcsec², and it has a physical half-light radius of about 577 light years. For comparison, this is about five times larger than the most extended globular clusters found in the Andromeda galaxy.
The galaxy is not perfectly round but exhibits an elliptical shape with an ellipticity value of 0.5. This projected elongation is aligned with a direction that is within 18 degrees of the line of sight toward Andromeda. The astronomers hypothesize that this elongation could be the result of past tidal interactions between Pegasus VII and the gravitational potential of the Andromeda galaxy, which may have stretched and deformed its shape over time.
Stellar Mass and Metallicity
In terms of stellar content, Pegasus VII has a relatively modest total stellar mass of around 26,000 solar masses. This is typical of dwarf galaxies, which tend to have far fewer stars compared to larger galaxies. Additionally, the metallicity of Pegasus VII is quite low, at −2.0 dex, indicating that its stars are relatively metal-poor compared to those in more evolved galaxies. This low metallicity is often found in older dwarf galaxies and is thought to reflect the early stages of galaxy formation when the abundance of heavier elements (such as iron and oxygen) was lower.
The age of Pegasus VII is estimated to be about 10 billion years, suggesting that the galaxy has been evolving for much of the universe’s history. Its relatively high age, combined with its low metallicity, implies that Pegasus VII may have formed early in the universe’s life, likely as part of the initial population of smaller galaxies that contributed to the assembly of larger galaxies like Andromeda.
Implications for Future Discoveries
The discovery of Pegasus VII provides further evidence for the presence of many more undetected dwarf galaxies in the halo of Andromeda. According to the study’s authors, the discovery is in line with both empirical and theoretical predictions that the halo of M31 contains a large number of undiscovered dwarf galaxy satellites. The researchers suggest that many more dwarf galaxies remain hidden, particularly those that are faint or located at greater distances from Andromeda.
The study of Pegasus VII, and similar dwarf galaxies in the future, will help astronomers better understand the formation and evolution of galaxies. In particular, these smaller galaxies are critical for understanding the hierarchical model of galaxy formation, which proposes that larger galaxies like Andromeda grew by merging with smaller galaxies over billions of years. By studying these faint and distant galaxies, scientists can gain insights into the early stages of galaxy assembly and the influence that large galaxies have on their smaller companions.
Conclusion
The discovery of Pegasus VII marks an exciting milestone in our understanding of dwarf galaxies and their role in the broader cosmic landscape. As the faintest known dwarf galaxy satellite of Andromeda, it offers a unique opportunity to study the physical properties, history, and interactions of these elusive objects. The findings also highlight the power of modern astronomical surveys, such as UNIONS, which continue to uncover hidden aspects of the universe that were previously beyond our reach.
With the ongoing development of more sensitive telescopes and surveys, astronomers are likely to uncover many more dwarf galaxies in the halo of Andromeda and other galaxies. Each discovery brings us one step closer to understanding the intricate processes that govern the formation and evolution of galaxies, helping to unravel the mysteries of the universe’s distant past. As we learn more about these faint, low-mass systems, we can deepen our understanding of the fundamental forces that shape the cosmos.
Reference: Simon E. T. Smith et al, Deep in the Fields of the Andromeda Halo: Discovery of the Pegasus VII dwarf galaxy in UNIONS, arXiv (2025). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2502.09792