When humanity first dreamed of reaching the stars, it was NASA—the National Aeronautics and Space Administration—that transformed those dreams into reality. From the moon landings to Mars rovers, NASA has been at the forefront of technological innovation. But NASA’s genius extends far beyond rockets and spacecraft. The agency’s relentless pursuit of knowledge has led to groundbreaking technologies that not only explore the cosmos but also transform everyday life here on Earth.
In this article, we’ll explore the 10 best space technologies developed by NASA—innovations that embody the spirit of exploration, the brilliance of human engineering, and the enduring drive to push the boundaries of the possible.
1. The Apollo Guidance Computer
One of the most revolutionary pieces of technology ever created by NASA was the Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC). This compact digital computer was a marvel of its time, designed to navigate astronauts safely to the Moon and back during the Apollo missions of the 1960s and 1970s.
Unlike the bulky mainframes of the era, the AGC was lightweight, efficient, and incredibly reliable. It introduced key concepts in computer science, such as integrated circuits, which are now the foundation of modern electronics. This little computer had just 64 KB of memory and operated at 0.043 MHz—yet it was powerful enough to guide astronauts through space with astonishing precision.
The AGC’s impact goes beyond space exploration. Its development accelerated the microchip revolution, paving the way for personal computers, smartphones, and virtually every digital device we rely on today. It was not just a navigation tool—it was the dawn of the digital age, inspired by humanity’s desire to set foot on another world.
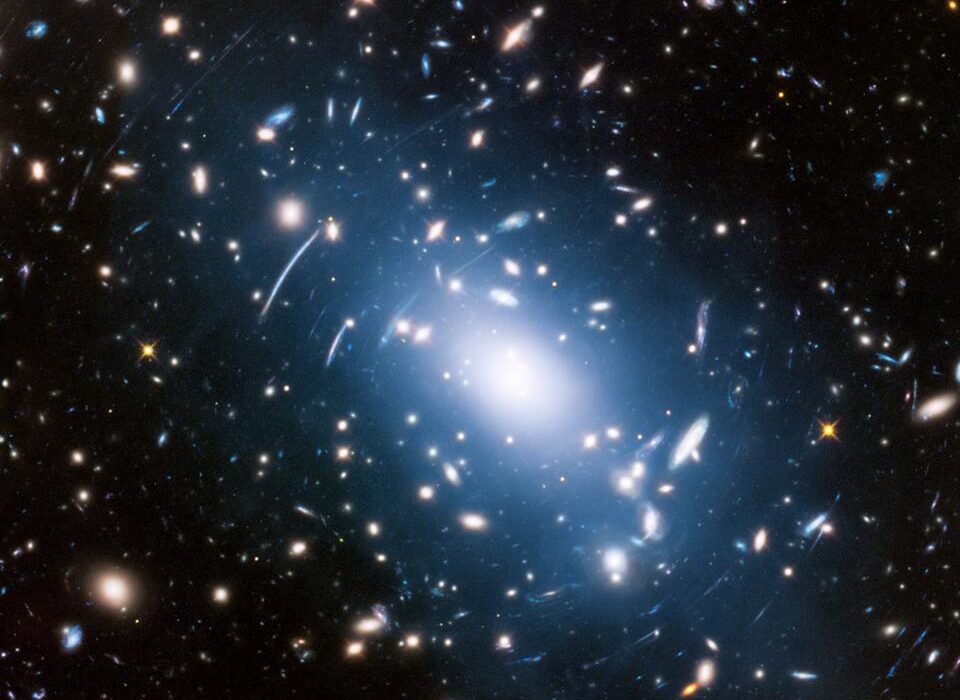
2. The Hubble Space Telescope
Few technologies have changed our understanding of the universe as profoundly as the Hubble Space Telescope. Launched in 1990, Hubble has been humanity’s eye in the cosmos for over three decades, capturing breathtaking images of distant galaxies, nebulae, and star systems.
Orbiting above Earth’s atmosphere, Hubble avoids the distortions caused by air and light pollution, giving it an unparalleled view of the universe. Its discoveries have been monumental: helping determine the age of the universe, providing evidence for the existence of dark energy, and revealing galaxies billions of light-years away.
Technologically, Hubble represents an engineering masterpiece. It has been serviced multiple times by astronauts, demonstrating NASA’s ingenuity in maintaining and upgrading complex instruments in space. Its data continues to fuel research, inspiring generations of scientists and space enthusiasts alike.
Hubble is more than a telescope—it’s a time machine, letting us peer back billions of years into cosmic history and deepening our connection with the universe.
3. The Space Shuttle
When the Space Shuttle first launched in 1981, it represented a bold leap forward in space technology. Unlike traditional rockets, which were single-use, the shuttle was reusable, capable of launching into orbit, carrying astronauts and cargo, and then gliding back to Earth like a plane.
Over its 30 years of service, the shuttle fleet flew 135 missions. They deployed satellites, carried parts for the International Space Station (ISS), conducted scientific experiments, and even repaired the Hubble Space Telescope. Each shuttle—Columbia, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour—became a symbol of human progress.
The shuttle program was not without tragedy, as the Challenger and Columbia disasters underscored the dangers of spaceflight. But the program’s technological achievements were extraordinary. It advanced thermal protection systems, robotic arms, space suits, and re-entry technologies, all of which continue to influence modern spacecraft design.
The Space Shuttle was not just a machine; it was a bridge between Earth and orbit, carrying humanity into an era of sustained space exploration.
4. Mars Rovers
When it comes to exploring distant worlds, NASA’s Mars rovers stand as some of the most extraordinary machines ever built. These robotic explorers have traveled across the Martian surface, conducting experiments, analyzing soil and rocks, and searching for signs of past water—and possibly life.
Starting with Sojourner in 1997, NASA’s rovers have grown more advanced with each mission. Spirit and Opportunity explored vast plains and craters, discovering evidence of ancient water. Curiosity, launched in 2011, continues to study the planet’s geology and atmosphere. And the most recent rover, Perseverance, has not only searched for signs of microbial life but also collected samples that may one day be returned to Earth.
Perhaps the most groundbreaking rover achievement is Ingenuity, the small helicopter carried by Perseverance. In 2021, Ingenuity made the first powered flight on another planet, proving that controlled flight is possible in the thin Martian atmosphere.
These rovers are more than robots—they are our emissaries on Mars, extending human curiosity across millions of miles of space.
5. The International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is one of the most ambitious engineering projects ever undertaken. Orbiting Earth since 1998, the ISS is a collaborative effort between NASA, Roscosmos, ESA, JAXA, and CSA, serving as a laboratory, observatory, and living habitat in space.
Technologically, the ISS is a marvel. It sustains life in the harsh environment of space, recycling air and water, generating power through solar arrays, and protecting astronauts from radiation. Its robotic systems, docking ports, and modular design enable continuous upgrades and international collaboration.
The ISS has hosted thousands of experiments across fields such as biology, physics, medicine, and materials science. Research conducted there has advanced our understanding of microgravity’s effects on the human body, paving the way for future missions to Mars and beyond.
Beyond science, the ISS is a symbol of what humanity can achieve when nations work together, transcending borders to explore the final frontier.
6. Space Suits
Behind every spacewalk, there is a technological marvel keeping astronauts alive: the space suit. Officially known as Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMUs), these suits are miniature spacecraft designed to protect humans in the vacuum of space.
NASA has continuously refined space suit technology since the Mercury and Apollo programs. Today’s suits provide life support, regulate temperature, shield astronauts from radiation, and supply oxygen—all while allowing mobility to perform complex tasks. The Apollo suits enabled astronauts to walk on the Moon, while modern EMUs allow astronauts to work on the ISS for hours at a time.
Currently, NASA is developing the next-generation Artemis suits, designed for Moon missions later this decade. These new suits will provide even greater mobility, durability, and flexibility to support long-term exploration.
Space suits are not just clothing—they are the difference between life and death in space, the armor of explorers stepping into the unknown.
7. The James Webb Space Telescope
If Hubble gave us a window into the universe, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) opened the door. Launched in December 2021, JWST is the most powerful telescope ever built, designed to peer deeper into the cosmos than ever before.
With its massive gold-coated mirror and ability to detect infrared light, JWST can observe the faintest galaxies formed just after the Big Bang, study the atmospheres of exoplanets, and uncover details invisible to Hubble. Already, JWST has delivered jaw-dropping images of galaxies, nebulae, and star systems, transforming our understanding of the universe’s infancy.
The technology behind JWST is staggering. Its mirror had to unfold in space like origami, and its five-layer sunshield is as large as a tennis court. Positioned a million miles from Earth, it must operate with incredible precision in extreme conditions.
JWST represents the pinnacle of human engineering, a triumph that allows us to glimpse the dawn of time itself.
8. NASA’s Satellite Technology
Satellites are the silent sentinels of modern life, and NASA has been a leader in developing satellite technology. From weather forecasting to global communications, GPS navigation to Earth monitoring, NASA’s satellites have reshaped our world.
The Landsat program, started in 1972, has provided continuous images of Earth, tracking environmental changes, deforestation, and urban growth. NASA’s climate satellites monitor rising sea levels, atmospheric conditions, and the health of our planet with unmatched accuracy.
Technologies developed for satellites—miniaturized sensors, advanced imaging systems, solar panels, and communication arrays—have become essential for civilian, commercial, and military applications worldwide.
Satellites may orbit silently above us, but their presence is woven into our daily lives, a legacy of NASA’s pioneering vision.
9. Ion Propulsion Systems
When it comes to interplanetary travel, traditional rockets aren’t enough. That’s where ion propulsion comes in—a technology NASA has been perfecting for decades.
Instead of burning chemical fuel, ion engines use electricity (often from solar panels) to accelerate ions to extremely high speeds, creating thrust. The thrust is small but continuous, allowing spacecraft to achieve incredible efficiency and speeds over long distances.
NASA’s Deep Space 1 mission in 1998 was the first to demonstrate ion propulsion, and the Dawn spacecraft later used it to visit two of the largest objects in the asteroid belt, Vesta and Ceres. Ion propulsion is now seen as a key technology for future missions to Mars and beyond.
This quiet, glowing blue engine is not just science fiction—it’s the future of deep space exploration.
10. Spinoff Technologies
Not all of NASA’s innovations remain in space. Many of its inventions have found their way into everyday life through what are known as NASA spinoffs.
Some of the most surprising examples include:
- Memory foam, originally developed to improve aircraft cushions, now used in mattresses and helmets.
- Scratch-resistant lenses, inspired by astronaut helmet visors.
- Infrared ear thermometers, based on sensors used to measure stars.
- Portable water filters, adapted from life-support systems on spacecraft.
- Cordless power tools, developed in partnership with Black & Decker for lunar missions.
These technologies prove that space exploration doesn’t just expand our horizons—it improves life on Earth in ways most people never imagine.
Conclusion
NASA’s technologies are more than machines and devices—they are the embodiment of human curiosity, courage, and creativity. From the Apollo computers that launched the digital age to the James Webb Telescope that peers back to the dawn of time, each innovation reflects our relentless drive to explore.
These ten technologies remind us that space exploration is not only about reaching the stars—it’s about transforming life here on Earth. They are proof that when humanity dares to dream big, we don’t just explore the universe; we reshape the future.