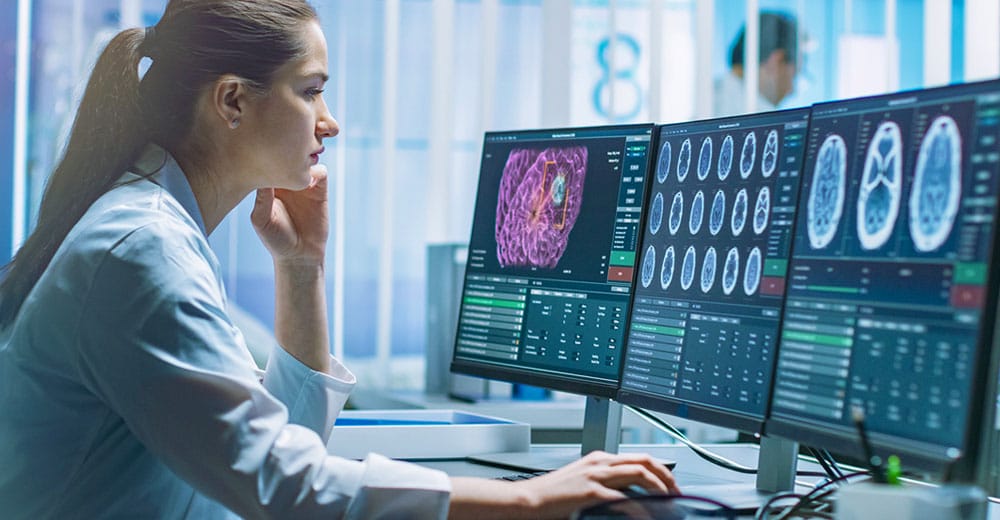
In a busy hospital in 2025, a doctor reviews a patient’s MRI scan. But instead of spending long hours poring over every detail, an AI system has already highlighted suspicious areas, ranked the likelihood of diseases, and even suggested the next best steps for treatment — all in the time it took the doctor to log in.
This isn’t science fiction anymore. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has quietly and then suddenly become one of the most powerful forces in healthcare. From predicting heart attacks before symptoms appear to discovering new life-saving drugs in months instead of decades, AI’s fingerprints are everywhere in modern medicine. It works silently in the background, supporting doctors, accelerating research, and sometimes saving lives in situations where human eyes alone would have missed the warning signs.
But AI in healthcare isn’t just about algorithms and data points — it’s about people. It’s about the father who gets to walk his daughter down the aisle because an AI system spotted a heart problem early. It’s about the cancer patient whose tumor shrinks thanks to an AI-designed drug. It’s about communities gaining access to quality healthcare even in remote corners of the world.
Here are 10 of the best and most inspiring examples of AI in healthcare today, blending science, technology, and humanity in ways that would have seemed impossible just a decade ago.
1. AI-Powered Medical Imaging: Seeing What the Eye Can’t
Medical imaging — from X-rays to MRIs — has always been one of the cornerstones of diagnosis. But the human eye, even trained for years, has its limits. Enter AI, with its ability to detect subtle patterns invisible to radiologists.
AI-powered image analysis systems like Google’s DeepMind Health and Arterys have achieved diagnostic accuracy rivaling — and in some cases surpassing — human experts. For example, DeepMind’s AI for breast cancer screening in mammograms reduced false positives by 5.7% and false negatives by 9.4% in clinical trials.
In one case, a patient in her 40s had a routine mammogram that showed no clear abnormality. The AI flagged a small irregular density that the radiologist initially dismissed. Follow-up testing confirmed an early-stage tumor — caught months, if not years, earlier than traditional methods would have allowed.
AI imaging doesn’t just work in wealthy urban hospitals. Portable ultrasound devices paired with AI analysis are now being used in rural clinics in Africa and Asia, giving communities access to diagnostic power once only available in top-tier medical centers.
2. Predictive Analytics for Early Disease Detection
Imagine being able to detect a disease before symptoms even begin. That’s exactly what predictive analytics powered by AI is making possible. By analyzing patterns in electronic health records, genetic data, wearable devices, and lifestyle factors, AI can calculate the probability of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, or stroke years in advance.
One standout example is IBM Watson Health’s predictive models for sepsis detection. Sepsis — a life-threatening reaction to infection — kills millions worldwide, often because it’s detected too late. Watson’s AI can analyze real-time patient data and flag early signs of sepsis up to 24 hours before traditional diagnosis, giving doctors a critical window to start treatment.
For patients, this means the difference between life and death. For healthcare systems, it means preventing costly, long hospital stays and improving overall patient outcomes.
3. AI in Drug Discovery: Compressing Decades into Months
Traditional drug discovery is notoriously slow, expensive, and uncertain. AI is changing that by scanning massive datasets of chemical structures, biological information, and disease pathways to identify promising drug candidates in record time.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, companies like BenevolentAI and Insilico Medicine used AI to pinpoint existing drugs that might combat the virus. BenevolentAI’s platform identified baricitinib — originally a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis — as a potential COVID-19 therapy. Clinical trials later confirmed its effectiveness in certain patient groups.
More broadly, AI platforms are now able to predict how molecules will interact with human proteins, reducing the need for countless failed experiments. This acceleration could mean that the next breakthrough cancer drug might be developed in years rather than decades.
4. Virtual Nursing Assistants: 24/7 Care Without the Wait
Patients often leave hospitals with a list of instructions — but questions and anxieties don’t follow office hours. AI-powered virtual nursing assistants like Sensely and Buoy Health provide round-the-clock support.
These systems can answer questions about symptoms, remind patients to take medications, schedule follow-ups, and even escalate urgent issues to human staff. The conversational AI is often paired with a friendly avatar, making the interaction feel personal rather than robotic.
For elderly patients living alone, such assistants can be a lifeline — a reassuring voice that helps them manage chronic conditions without feeling abandoned between doctor visits.
5. Personalized Treatment Plans Through AI
No two patients are exactly alike, and medicine is slowly moving away from the one-size-fits-all approach. AI-driven platforms can integrate genetic data, lifestyle habits, and even microbiome analysis to design personalized treatment plans.
In oncology, for instance, IBM Watson for Oncology analyzes patient records and medical literature to recommend treatment strategies tailored to an individual’s genetic profile. A lung cancer patient, for example, might be matched with a specific targeted therapy based on their tumor’s mutations, improving survival rates and minimizing side effects.
The emotional impact here is profound — patients feel seen, understood, and treated as unique individuals rather than just cases in a database.
6. AI-Enhanced Surgical Precision
In the operating room, precision is everything. AI is now assisting surgeons by providing real-time guidance, predicting potential complications, and even automating certain parts of procedures.
Robotic surgery systems like da Vinci Surgical System, when paired with AI, can identify anatomical structures, suggest optimal cutting paths, and ensure minimal damage to surrounding tissues. In brain surgery, AI can map neural pathways to avoid critical regions, reducing the risk of post-operative deficits.
For patients, this often means shorter recovery times, fewer complications, and better long-term outcomes — and for surgeons, an invaluable second set of “eyes” that never tires or blinks.
7. AI for Mental Health Support
Mental health care faces a global shortage of professionals. AI tools are helping bridge that gap by providing scalable, accessible support. Apps like Woebot use conversational AI to deliver cognitive behavioral therapy techniques, track mood patterns, and offer coping strategies.
These aren’t replacements for human therapists but valuable supplements. In areas where access to mental health services is limited, AI can be the first line of support — and sometimes the only one. For someone struggling with anxiety at 2 a.m., an empathetic, responsive chatbot can be a step toward stability until professional help is available.
8. AI in Pathology: A Revolution Under the Microscope
Pathologists examine tissue samples to diagnose diseases, but the sheer volume of samples can lead to delays and fatigue-related errors. AI algorithms can scan digital pathology slides at incredible speed, detecting cancer cells or other abnormalities with remarkable accuracy.
For example, Google Health’s AI system for detecting breast cancer metastases in lymph nodes outperformed human pathologists in certain trials, spotting micrometastases that might otherwise be missed.
In one real-world scenario, a young patient’s aggressive cancer was caught earlier than it would have been by human review alone, enabling immediate treatment and vastly improving her prognosis.
9. AI for Pandemic Prediction and Response
COVID-19 was a wake-up call for global health systems. AI now plays a key role in monitoring disease outbreaks by analyzing news reports, flight patterns, social media data, and even wastewater analysis.
BlueDot, a Canadian company, famously alerted its clients about the COVID-19 outbreak days before the World Health Organization issued its first official warning. Such early warnings allow governments and hospitals to prepare resources, control spread, and potentially save thousands of lives.
In the future, AI could act as a global immune system — constantly scanning for the earliest signs of new threats and giving humanity a head start in fighting them.
10. AI for Administrative Efficiency
While less glamorous than robot surgeons, AI in healthcare administration is a quiet revolution that frees doctors to spend more time with patients. Automated systems can handle appointment scheduling, billing, insurance claims, and even transcribing medical notes via speech recognition.
For example, Nuance’s Dragon Medical One transcribes doctors’ speech into accurate medical records in real time, reducing paperwork hours and burnout. For overworked healthcare professionals, this isn’t just convenience — it’s the difference between spending an evening with family or being stuck at the clinic doing documentation.
Conclusion: The Heart in the Machine
The best uses of AI in healthcare aren’t about replacing humans — they’re about amplifying human abilities. The technology’s power lies in its ability to handle complexity, spot patterns, and tirelessly support doctors and nurses in their mission to heal.
Yet, as we celebrate these breakthroughs, it’s important to remember that AI is a tool, not a miracle cure. Ethical safeguards, data privacy, and equitable access must guide its implementation.
If we get it right, AI won’t just change medicine — it will transform what it means to be a patient, a doctor, and even a community. It will give us a future where care is not only faster and more precise but also more compassionate, because the machines will take on the burden of data, leaving humans free to do what they do best: care for each other.