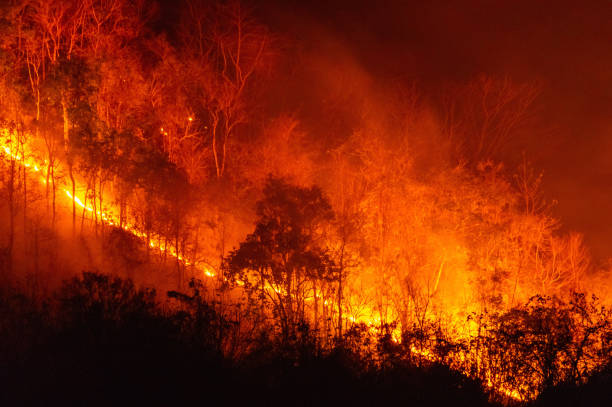
In recent decades, the images have become heartbreakingly familiar: vast landscapes consumed by roaring flames, skies turned an eerie orange, families fleeing their homes, wildlife running from their burning habitats, and firefighters battling seemingly unstoppable infernos. Wildfires, once seasonal and somewhat predictable, are now escalating in frequency, intensity, and scale, driven by a warming climate, drier conditions, and shifting weather patterns. From California’s forests to the Australian bush, from the Mediterranean hills to Siberia’s tundra, the Earth has become increasingly vulnerable to fire’s devastating grip.
The tragedy of wildfires extends far beyond charred trees. They claim lives, destroy communities, pollute air with toxic smoke, threaten biodiversity, and contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. For many, the fire season is no longer a temporary crisis but a recurring nightmare. The urgency for innovative solutions is greater than ever. Amid this urgency, artificial intelligence—AI—emerges not as a silver bullet but as a powerful ally, offering the possibility of predicting, preventing, and responding to wildfires with unprecedented speed and precision.
Understanding the Challenge
To appreciate the role of AI in wildfire management, one must first understand the challenge itself. Wildfires are not simple phenomena. They are the result of a complex interplay of weather, vegetation, topography, and human activity. A single spark—whether from a lightning strike, a downed power line, or an unattended campfire—can ignite a blaze that grows exponentially under the right conditions. Wind speed, humidity, slope of the land, and dryness of vegetation all determine whether that spark fizzles or erupts into a catastrophic inferno.
The difficulty lies in scale and unpredictability. Forests cover vast territories, much of them remote and inaccessible. Weather conditions change rapidly. Fires spread erratically, sometimes jumping rivers and highways, at other times smoldering unseen underground. Human detection often comes too late—by the time smoke is spotted, the fire may already be beyond control. Traditional monitoring systems, though valuable, cannot match the speed and scale at which fire can move.
This is where AI shows its promise: in transforming an overwhelming flood of environmental data into actionable intelligence, in recognizing patterns invisible to human eyes, and in enabling proactive strategies rather than reactive scrambling.
AI as the Eyes of the Forest
One of AI’s greatest contributions is in wildfire detection and monitoring. Forests cannot be everywhere watched by human eyes, but they can be blanketed by networks of sensors, cameras, satellites, and drones, each producing streams of data that AI can process in real time.
Satellites orbiting Earth capture images across multiple wavelengths—visible light, infrared, and even thermal signatures. While humans might only notice smoke, AI algorithms can detect subtle heat anomalies before flames are visible, flagging potential ignitions long before they spiral out of control. Machine learning models trained on vast datasets of past wildfires can distinguish between harmless hot surfaces and genuine threats, reducing false alarms that would otherwise overwhelm responders.
In addition to satellites, ground-based cameras and drones provide closer views. AI-enhanced image recognition can analyze live video feeds, identifying the telltale signs of smoke plumes even in their earliest stages. Unlike human observers, who may grow tired or miss small details, AI never rests, scanning continuously and alerting authorities the moment a suspicious signal appears.
The result is a kind of artificial vigilance—an unblinking watch over forests and grasslands, where every unusual flicker of heat or wisp of smoke is noticed and reported. In wildfire management, minutes matter; AI buys those precious minutes.
Forecasting Fire Before It Burns
Beyond detection, AI excels in prediction. Using historical fire data, weather forecasts, vegetation maps, and even social patterns of human behavior, AI models can estimate not only where fires are most likely to start but also how they will behave once ignited.
Predictive models simulate fire spread across landscapes, accounting for wind direction, humidity, terrain slope, and available fuel. These simulations allow emergency services to anticipate the fire’s path, allocate resources efficiently, and issue timely evacuation warnings. Instead of reacting blindly to fast-moving flames, firefighters can be positioned strategically, and communities can be warned with life-saving precision.
AI-powered forecasting also helps with prevention. By identifying high-risk zones before fire season begins, land managers can prioritize controlled burns, vegetation clearing, and infrastructure maintenance, reducing the chances of a spark turning into a disaster. In California, for instance, utilities are beginning to use AI models to assess the fire risks posed by power lines, guiding maintenance schedules and reducing the risk of equipment-induced ignitions.
In this way, AI transforms wildfire management from a game of catch-up into one of foresight. It turns data into a shield, enabling societies to act before the flames do.
AI on the Frontlines
When wildfires break out despite best efforts, response speed is crucial. Here too, AI is revolutionizing the battlefield.
Autonomous drones, guided by AI, can be deployed into dangerous zones where human pilots cannot go. They map fire perimeters in real time, providing updated information about its spread, intensity, and behavior. This information feeds back to command centers, where AI systems continuously update predictive models, helping leaders make rapid, evidence-based decisions.
AI also helps coordinate resources. Large fires often involve dozens of agencies, hundreds of vehicles, and thousands of personnel. The logistics of directing such an operation are staggering. AI-driven decision support systems can process incoming data faster than human operators, suggesting optimal deployment strategies for firefighters, aircraft, and equipment. By analyzing traffic conditions, wind forecasts, and fire growth projections, AI can guide decisions that save both lives and property.
Even the aircraft that drop water or fire retardants are beginning to benefit from AI-assisted navigation systems. These systems calculate the best drop zones with pinpoint accuracy, maximizing effectiveness while minimizing wasted effort. In an environment where every liter of water and every second counts, such precision makes a difference.
The Role of AI in Community Safety
AI is not only about fighting fires but also about protecting people from them. Smart evacuation systems are being developed that use AI to predict which routes will remain open as fires spread. By integrating real-time traffic data, fire models, and communication networks, these systems can guide communities along the safest possible paths, avoiding bottlenecks and panic.
In addition, AI can power early-warning apps that send alerts directly to residents’ phones, providing updates tailored to their location. These apps can deliver not only warnings but also practical instructions, such as where to find shelters or when to evacuate. For vulnerable populations—elderly residents, people with disabilities, or those without personal transportation—AI-assisted planning can ensure that evacuation strategies account for their needs in advance, reducing tragic outcomes.
Public communication is also enhanced by AI. Natural language processing tools can sift through social media posts during emergencies, identifying cries for help, mapping hotspots of concern, and detecting misinformation that could endanger lives. In this way, AI becomes a partner not just in firefighting but in protecting communities’ hearts and minds.
Protecting Nature’s Balance
Wildfires do not only threaten human lives and infrastructure; they endanger ecosystems that sustain biodiversity and regulate our planet’s climate. Entire species can be pushed toward extinction by repeated fires, while carbon-rich forests, when burned, release massive amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
AI-driven conservation strategies are helping scientists monitor post-fire recovery, track wildlife movements, and prioritize areas for reforestation. By analyzing drone footage and satellite data, AI can assess which regions need urgent attention, guiding restoration efforts more effectively. It can also help distinguish between natural fire regimes, which ecosystems may rely upon for renewal, and destructive, climate-driven megafires that destabilize ecological balance.
Thus, AI does more than fight against fire—it helps us live in harmony with the cycles of nature, protecting both human society and the natural world on which it depends.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers remarkable potential, it is not without challenges. Developing accurate predictive models requires vast amounts of high-quality data, yet in many regions, such data is incomplete or inaccessible. Integrating AI systems into existing emergency frameworks requires training, trust, and investment, all of which can be difficult in underfunded fire-prone areas.
There are also ethical questions. Who owns the data collected by satellites and sensors? How do we ensure AI decisions are transparent and accountable, especially when human lives are at stake? What happens if predictive models fail, either by overestimating risks and causing unnecessary evacuations or by underestimating them and leaving communities vulnerable?
These concerns remind us that AI is a tool, not a savior. It is most effective when combined with human judgment, local knowledge, and strong community resilience. Technology must be deployed thoughtfully, with respect for privacy, equity, and ecological balance.
A Glimpse of the Future
Looking ahead, the role of AI in wildfire prevention and response will only deepen. Future systems may integrate even more diverse data sources: Internet-of-Things sensors embedded in forests, high-resolution satellite constellations providing continuous coverage, and even AI-powered climate models that anticipate fire conditions months in advance.
We may see fleets of autonomous firefighting drones capable of not just mapping but also suppressing small fires before they grow. Communities may rely on AI-powered digital twins—virtual replicas of their landscapes—allowing them to simulate fire scenarios and prepare accordingly. Global collaborations may emerge, where AI systems share data across borders, enabling a collective defense against a threat that knows no boundaries.
The dream is not a world without fire—fire is, after all, a natural force—but a world where fire no longer spirals into catastrophe, where human ingenuity and artificial intelligence combine to safeguard both people and planet.
Conclusion: Intelligence in the Flames
The story of wildfire is a story of destruction and resilience, tragedy and hope. In the face of growing infernos, humanity is called to act with both urgency and wisdom. Artificial intelligence does not replace that wisdom, but it amplifies it. It gives us new eyes to see danger before it strikes, new tools to respond when flames rise, and new possibilities for building safer, more resilient communities.
To harness AI for wildfire prevention and rapid response is to embrace both science and compassion. It is a recognition that while we cannot control the wind or the spark, we can control how we prepare, predict, and protect. And in doing so, we honor not only our survival but also the forests, animals, and landscapes that share this fragile planet with us.
In every flicker of flame there is danger, but in every breakthrough of knowledge there is hope. AI is not just about machines—it is about humanity’s determination to face fire with intelligence, courage, and unity.